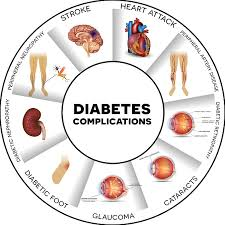
Diabetes, while manageable, can lead to serious complications if not well-controlled. This blog post will delve into both acute and chronic complications of diabetes, strategies for prevention, and essential patient education.
Acute Diabetes Complications
-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA):
- Occurs when the body doesn't produce enough insulin.
- Symptoms include: frequent urination, excessive thirst, nausea, vomiting, and fruity-smelling breath.
- Treatment involves immediate medical attention, including insulin therapy and fluid replacement.
-
Hypoglycemia:
- Results from low blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms include: sweating, shaking, dizziness, and confusion.
- Treatment involves consuming fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets or sugary drinks.
Chronic Diabetes Complications
-
Cardiovascular Disease:
- Diabetes increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Prevention strategies include: managing blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
-
Kidney Disease:
- High blood sugar can damage the kidneys.
- Prevention involves controlling blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
-
Neuropathy:
- Nerve damage can cause numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Regular foot exams and good foot care are crucial.
-
Retinopathy:
- Damage to the blood vessels in the retina can lead to vision loss.
- Regular eye exams are essential.
Preventing Diabetes Complications
- Strict Blood Sugar Control: Regular monitoring and medication adherence are key.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in sugar and saturated fats can help.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of complications.
- Manage Stress: Stress can affect blood sugar levels.
Patient Education: Empowering Diabetes Self-Management
-
Self-Care:
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- Adhering to medication regimens
- Following a healthy diet and exercise plan
- Managing stress
-
Effective Communication:
- Open communication with healthcare providers
- Sharing concerns and questions with healthcare team
- Involving family and friends in the management process
-
Problem-Solving:
- Identifying potential barriers to self-management
- Developing strategies to overcome challenges
- Seeking support from healthcare providers or diabetes educators
Advanced Diabetes Management Topics
-
Insulin Pump Therapy:
- Delivers insulin continuously, mimicking the body's natural insulin production.
- Offers flexibility and improved blood sugar control.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM):
- Provides real-time glucose readings, allowing for timely adjustments to insulin therapy.
- Helps prevent hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
-
Diabetes in Special Populations:
- Pregnancy: Requires careful monitoring and management to ensure healthy outcomes for both mother and baby.
- Children: Pediatric diabetes management involves specialized care and education.
- Older Adults: Aging can impact diabetes management, necessitating adjustments to treatment plans.